
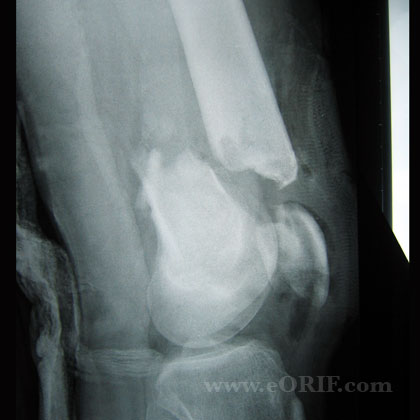
6,8 CRPP fixation of type IB fractures was also recommended if varus malunion seems possible. Although the initial recommendation was weak based on quality of the available literature, pin fixation with displaced fractures were superior in preventing cubitus varus and loss of motion.Īlthough the AAOS Guidelines did not address Type IB injuries, these injuries might have a tendency to collapse into varus due to the comminution of the medial column. 8 A moderate recommendation for CRPP fixation was given to any displaced fracture (Gartland Type II and Type III). The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) has recently published Guidelines on the treatment of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. The rationale for closed reduction and percutaneous pinning is that the distal fragment can be controlled by the pin fixation to decrease the incidence of varus malunion, while the arm can be positioned in a comfortable semi-extended position at the elbow, avoiding discomfort and complications associated with flexing an elbow against a swollen antecubital fossa. Minimally displaced fragments with medial column comminution or any malalignment in the coronal plane.Minimally displaced fragment in which capitellum is posterior to the anterior humeral line.Summary of indications for closed reduction percutaneous pinning (CRPP): Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier 2008. From Herring JA: Tachdjan’s Pediatric Orthopaedics from the Texas Scottish Rite Hospital for Children: 4th ed. Classification of supracondylar fractures of the humerus, as described by Gartland in 1959. The senior author prefers to classify supracondylar fractures as either displaced or undisplaced.įigure 1. 7ĭespite being commonly used descriptively, the Gartland classification is not validated, nor does it clearly guide clinical care. A recent addition to this classification is a Type IV fracture in which the distal fragment is unstable in both flexion and extension due to the loss of the periosteal attachments. Type III injuries can also be further delineated to either posteromedial or posterolateral injuries. 6 Some clinicians distinguish between a Type IIA fracture, which is angulated with an intact hinge of bone, and a Type IIB fracture, which has a complete fracture line with displacement but with the distal fragment still touching the end of the proximal fragment. For example, the Type IA has been described as a truly nondisplaced fracture and the Type IB as a minimally displaced fracture with medial column comminution or varus collapse. There have been several modifications of the Gartland classification over the years. A Type III injury is a completely displaced fragment.A Type II fracture is a displaced fragment with an intact posterior cortex (ie, intact hinge).A Type I fractures is nondisplaced or minimally displaced.Gartland originally classified extension-type fractures, and his system remains the most widely used (Figure 1). More common are the extension-type supracondylar humerus fractures.Flexion-type supracondylar humerus fractures account for only 2% to 5% of these injuries. A flexion supracondylar humerus fracture is when the distal fracture is either flexed, or displaced anteriorly, to the proximal shaft of the humerus.3 Classificationįractures of the supracondylar humerus are first classified as either flexion or extension injuries. 1,2 A supracondylar fracture of the humerus typically occurs by a fall on an outstretched hand from either furniture (beds, couches, or other objects 3-6 feet high) or playground equipment (monkey bars, slides, or swings). This injury accounts for 50% to 70% of all elbow fractures in children and 3% to 7% of all fractures. A supracondylar humerus fracture is an extra-articular fracture of the distal humerus at the elbow that typically occurs in children between the ages of 5 and 9 years old.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
